Human hair structure. Hair: structure and function
Look shiny and well-groomed can only really healthy hair. Girls often, wanting to help their tresses begin to take care of them with the help of many expensive tools, but do not get the desired result. This may be due to a simple lack of knowledge on the diet of the scalp, the structure of the vegetation and its roots.
Having studied the structure of human hair on the head, can be more effectively they feed and grow.
Overview of the hair and scalp
Each person has the whole body is covered with tiny hairs. The only exceptions are the flexor surface of the lips, the lateral surfaces of the fingers, nail phalanges, hands and feet. In some places the hair coat is barely noticeable, in others - it grows only to a certain color.
Before considering the structure of the hair, you need to understand what their functions are performed by the nutrient medium, ie the skin.
The structure of the scalp
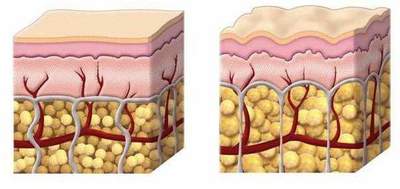
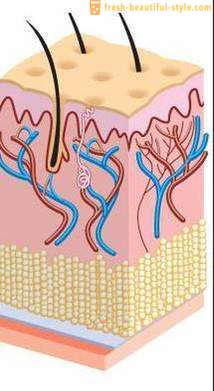
The skin covers the whole body, it is about 5% of body weight. On the head of this body is made up of several layers, which in turn, further divided into finer education.

1. The epidermis (upper layer consists of partially dead cells that are removed during washing):
- basal layer;
- grainy;
- shining;
- horny.
2. Dermis (upper layer having blood vessels and nerve endings). It contains a well-known protein called collagen, which gives skin elasticity and smoothness.
3. hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). Its main function is to provide thermal regulation.
The cells of the basal layer of the epidermis are two periods updates throughout the day: in the morning and in the afternoon up to 15 hours. At this time, the cortisol level is low. This period is considered the most favorable for the care of the scalp and body.
Functions of the skin of the head
1. Security. Skin protects the body fat from being hit by harmful microorganisms. The epidermis prevents mechanical damage.
2. The immune. T lymphocytes detect endogenous and exogenous antigens. Largengansa cells of foreign bodies are transported to the lymph nodes, where they are neutralized.
3. Receptor. The skin's ability to perceive and recognize the tactile and thermal stimuli.
4. Exchange. The skin breathes and develops through the sebaceous and sweat glands secrets, creating on the surface of a thin film.
5. Thermostatic. During the temperature rise outside of the skin vessels dilate, which increases the heat transfer. A significant reduction in temperature causes the slow blood flow and thereby reduce evaporation.
After studying the structure and function of the scalp becomes clear that for normal hair growth should have as a healthy foundation, retaining them. Its power can be carried out in two ways: internal and external. Given that the outer layer of skin is composed mainly of dead cells that are no longer needed food, becomes relevant supply of it from the inside with vitamins and minerals. To do this, you need to eat right, and take additional natural vitamin complexes, if necessary.
Hair: structure and function
Each hair is most of the protein keratin. Also in the always have a certain amount of water, traces of metals and minerals.
The structure of a human hair
Hair represent horny skin formation. They are present only in humans and mammals. Whisker formation surface of the head cover portion.
To study the structure of the hair can be under the microscope. It should be borne in mind that, considering the scalp, you can not just see. Beneath it is hidden a very important part - the root. Therefore, considering the structure of the hair, it is necessary to study their internal and external components. Read about it on.
Hair Structure: the outer part of
It has three layers:
1. The core (inner part) is composed of non-cornified cells.
2. The cortex (cortical layer) is 90% by weight of the hair. It consists of elongated cells. It is here that contains melanin, which is responsible for a certain hair color.
3. The cuticle (outer layer) structurally resembles flakes lumps or shingles, wherein each bit of the next part of the same area with the previous one.
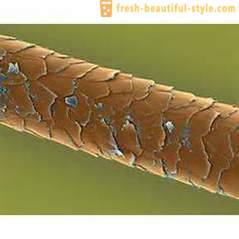
These particles are arranged in 6-9 layers, which are attached with a certain composition. Scales grow from the root to the ends. It is this layer so nice shine, when the hair is healthy, that is, all the particles lie flat and reflect light. Its main function is to protect the inside of the hair.
A natural antiseptic, which is part of grease, additional protection against the penetration of the cortex infections. The structure of the hair shaft is very dependent on the state of human internal environment. During many diseases hair condition is deteriorating rapidly, precisely because of their inner and outer layer of the stops do enough vitamins.
It is worth knowing that the core contains not all the hair. For example, in a light gun is not.
The structure of the hair: the inside of the
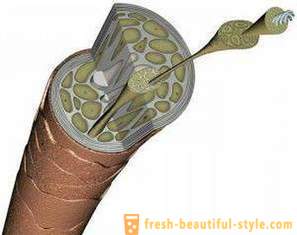
Each hair grows from its own follicle. It is also possible to name a matrix for cell growth.
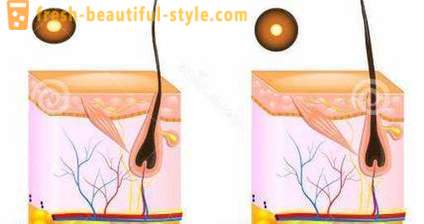
The structure of the hair root to the form of a bag. Hair will grow in length, it is still alive its root, located in the scalp.
The follicle is the recess which contains the root. "Bag" expands downward, forming the hair follicle. This fit portion blood vessels, sebaceous and sweat glands. All of them provide the power and output of waste products. On the inner side located follicle dermal papilla, which consists of very thin blood vessels, and nerve connective tissue.
This is the structure of the hair. Photo clearly shows this.
Hair functions
1. Security. During direct sunlight thanks to the hair on the skin does not penetrate ultraviolet.
2. Thermoregulation. Before the invention of warm clothing for cold people defended it hair. On the head they maintain a comfortable temperature for normal brain function. This structure of human hair is not accidental. Upon cooling rectifying muscles lift the hair, and they do not give rise own heat from the skin.
3. Touch. A large number of nerve endings in the scalp making it sensitive to the smallest changes in the hair situation. Especially it can be seen when it is crawling insect.
Hair Growth Stages
1. Anagen (2-4 years). At this time, there is the greatest activity of the follicle, as there is intense cell division and growth. As a result, the hair is growing. In some cases this stage lasts up to 5 years. In a healthy person about 85-90% of the hair have the age.
2. Catagen (15-20 days). At this stage the follicle activity is reduced, but the papilla cells are still functioning poorly. By the end of the bulb is detached from the power supply of the papilla. Only 1% of the hair is in this phase.
3. Telogen (90-120 days). During this time, the cell no longer share in the hair root and hair bulb leaves his seat with the rod.

After that, the formed free space anagen phase begins the new follicle.
Features of growth are still in the angle at which the stem grows. The structure of the scalp and hair in combination can output the tube at an angle of 10 to 90 °. That is why some women simply can not afford to make yourself a bulk packing. This means that most of their hair grow at an angle of 10-20 °, and simply can not meet in the opposite direction. This problem manifests itself in men in the inflamed areas on the face. They are ingrown hairs, which have not been able to rise above the surface of the skin.
The structure of the hair on the head is a little different from their counterparts elsewhere in the body. For example, they are able to withstand loads of up to 200 grams, it shows their strength. On elasticity indicates the possibility of styling hair in all sorts of hairstyles.
The thickness of the hair and the amount of
Structure of human hair on the head to some extent determined by their color. The thickness of the rod at the red about 100 microns, at mans - 75 microns, y blond - 50 microns.
The number of rods on the head in different people is 100-150 thousand. It is genetically determined.
hair form, that is, the presence or absence of curls or just waves determined by the characteristics of the follicle position relative to the surface of the head.
Therefore, to study the structure of the skin and hair of the person, it becomes clear how to care for them, feed, stow and at what time it is desirable to do.